What is the Accuracy of 3D Laser Scanning?

posted 19th June 2024

3D laser scanners are modern surveying technology used in construction projects. They are an advancement on traditional hand surveying methods. Many people ask the question, “what is the accuracy of 3D laser scanning?” Your questions and more are addressed in this post.
Precision 3D Laser Scanning
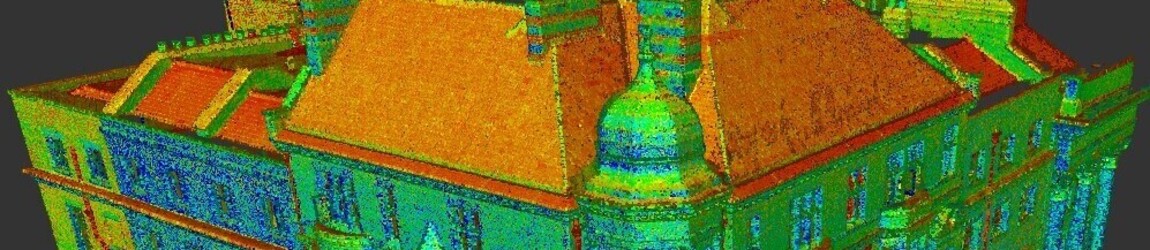
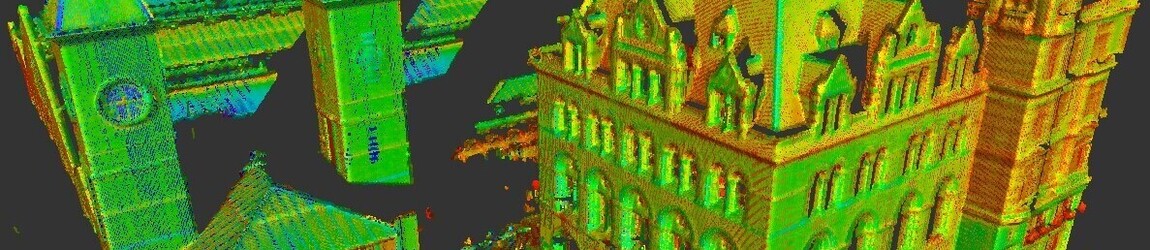
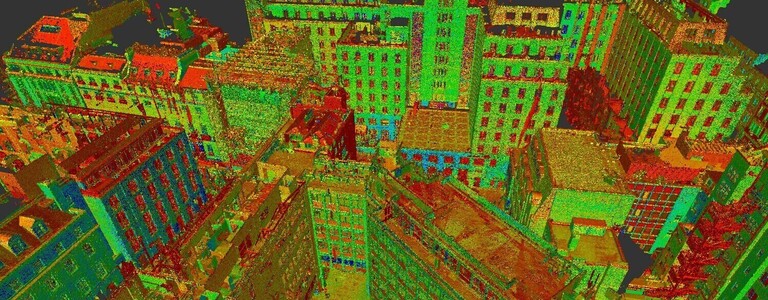
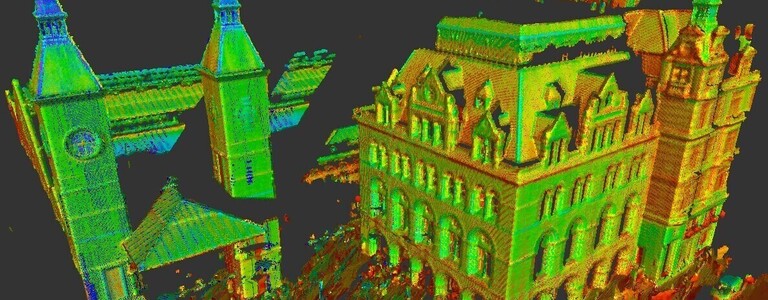
3D laser scanning uses high definition laser scanning technology that captures and records millions of data points with the aim of creating a full and accurate 3D image of a structure or building. The data forms the basis for production of models and plans, along with elevations and sections.
This technology uses LIDAR (Light, Imaging, Detection, and Ranging) technology. It is able to capture high volumes of data in a short time frame. In a few seconds, these scanners can capture up to two million data points in high resolution.
How Does 3D Laser Scanning Work?
3D laser scanning technology records data points that are within its field of vision, building a point cloud of a building or structure. The recorded points carry valuable x, y, and z co-ordinates.
A complete survey is made up of numerous scans taken from various locations, providing a line of sight survey. Each point cloud is stitched together with up to 2mm precision, using software to create an accurate point cloud.
These surveys save time on site, providing a high volume of useful information. The scanner will pick up everything within its line of sight, meaning that information not required for the current survey can be stored and used in the future without the engineer having to return to the building site.
What is the Accuracy of 3D Laser Scanning?
3D laser scanning is able to provide the most detailed and precise data sets. The process is more than doors, windows and walls. It provides accurate details that you can see the features in high resolution. .These scanner capture everything from power sockets to architectural mouldings, and everything in between.
These scanners, using advanced technology, are able to provide accurate within 2mm, though the final accuracy can only be measured based on the final point cloud, which tends to be slightly less.
The accuracy is actually impacted by a number of factors including ground stability, surfaces, materials, and environmental factors. The skill and experience of the surveyor also plays a role in the accuracy, both on site and in the office.
The software cannot produce accuracy without human input. An accurate 3D laser scan will offer an accuracy of up to 2mm, while a bad scan could have up to 30mm in error. This can be due to poor registration techniques or site techniques.
How the data is interpreted and producing drawings also leads to the risk of inaccuracies. As a result, it is imperative that any 3D laser scanning surveys be carried out by experienced, trained, and skilled surveyors, as errors are more likely experienced when the surveyor is not skilled on the scanners operation.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning surveys have become an essential part of construction projects and require the highest level of accuracy. Identifying potential problems before the build starts is invaluable, helping property owners save money in the long run. 3D laser scanning offers fast solutions, recording thousands of data points per second with a 2mm accuracy.