How Does 3D Laser Scanning Work?

posted 18th June 2024

3D laser scanning is an important first step to any successful construction project. It is used by construction teams, architects, and engineers, documenting the existing condition of any structure.
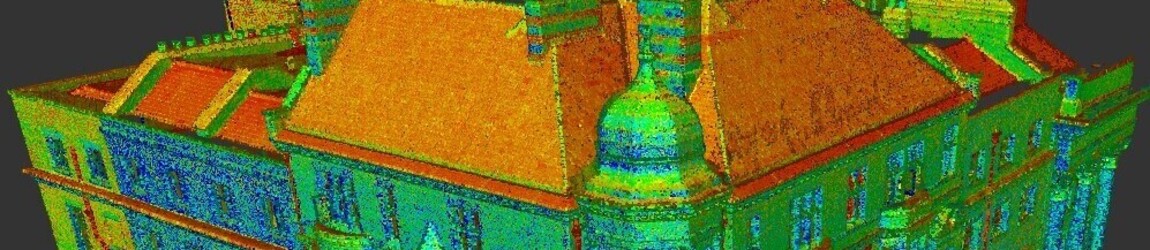
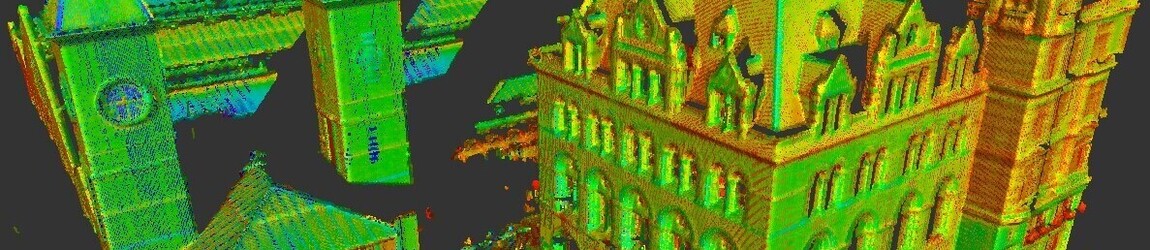
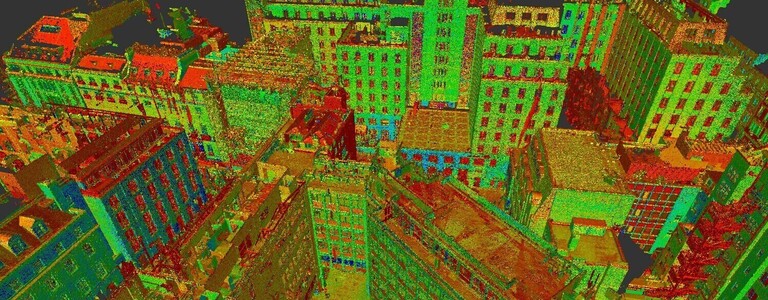
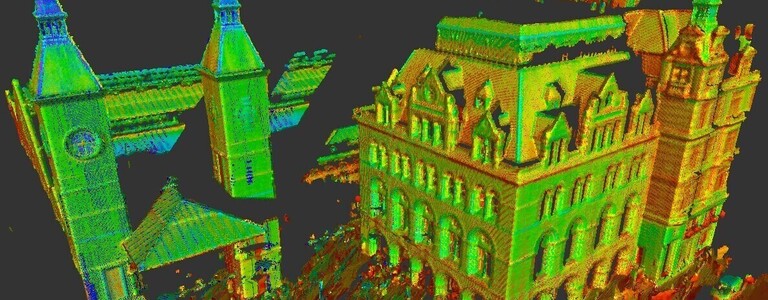
These laser scanners use Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) that measures and records locations and distances with precise results, producing a point cloud file. The 3D laser scanners are lightweight and mobile, offering accurate digital measurements and measurements. They are easy and quick. The data collected is valuable to any design.
How Do 3D Laser Scanners Work?
Laser scanners send light pulses at a very high speed. These light pulses reflect off objects and return to the LIDAR sensor. Each pulse measures the distance between the object and the scanner. This is done by determining the time between the send and receive pulse. Each data point is then converted to a pixel with a known x,y, and z coordinate.
The scans are taken in multiple positions throughout the site and from a variety of viewpoints. Millions of data points and captures and processed to create an accurate 3D map. This happens quickly with most scanners, some are able to capture and calculate up to two million points per second with 2mm accuracy.
How the Data Will Be Used
Before any new build starts, 3D laser scanners are used, as it is the most efficient way to generate data points for modelling and mapping. It does require a trained and skilled technician that will spend anywhere from a few hours to a few days on-site capturing all the data required. Engineers then create the maps and models, from CAD drawings to 3D virtual tours.
High resolution scans are often needed to conduct building surveys on historical or listed building. These need to be high resolution and highly accurate. It provides precise building details for restoration projects.
3D Laser Scanning Applications
There is a number of laser scanning applications. The most common way 3D laser scanning is used includes:
- Existing conditions surveys
- Construction verification
- Design for upgrades and expansions
- 2D or 3D mapping of an existing building
- Architectural documentation for historical buildings
- Design and construction
How Does This Technology Work?
Project managers use professional 3D laser scanners for engineering, industrial, construction projects, and architectural projects, offering excellent speed, data quality, and range. The majority of these scanners provide accuracy of two to four millimetres and can be tied to survey controls.
The scanners are very lightweight and provide flexibility when on-site. All operators receive training to ensure that they can use the full capabilities of these scanners, providing clients with accurate measurements.
There is a variety of makes and models when it comes to these scanners, though they all tend to work the same. They look like cameras, placed on tripods, containing highly sensitive laser and panoramic HD cameras, capturing the spaces in real time.
The good news is that the laser cannot cause harm to people, animals, or buildings, making them ideal to survey listed properties. The scanners rotate at lightening speeds inside the casing, capturing up to two million data points in a single second, depending on the scan resolution. The beam interacts with the space features, recording it as a data point.
The data points are referred to as point clouds. The more points captured, the higher the resolution and accuracy. The resolution is determined by how the scan is to be used.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning is often one of the first steps to any building project. This type of recording is accurate and precise, while improving site safety, eliminating the need for human measurements, which can incur errors, and reducing the number of site visits.