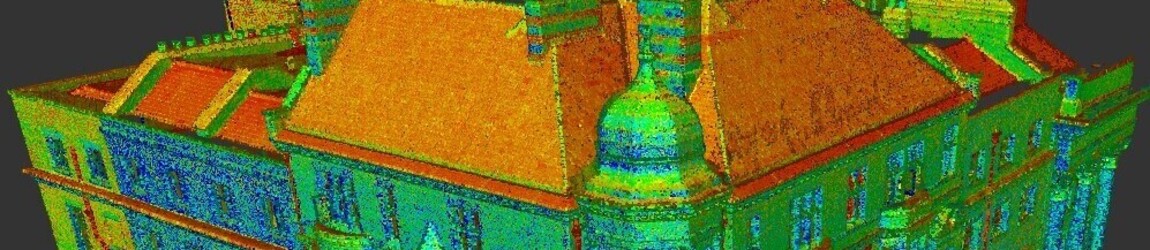
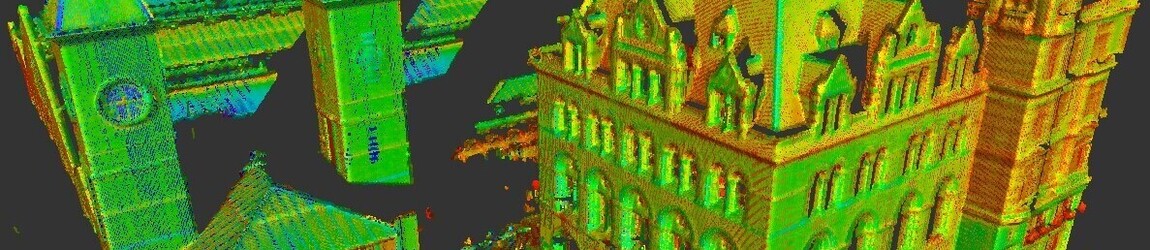
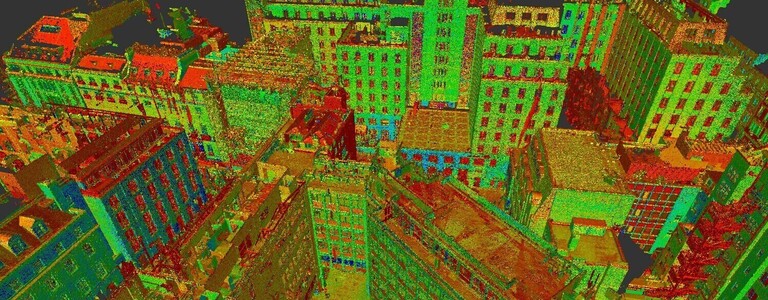
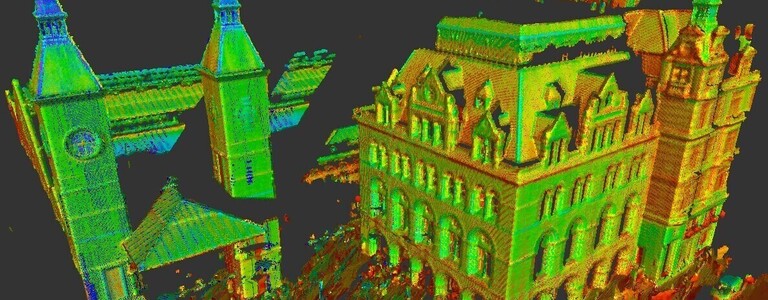
How Accurate is 3D Laser Scanning?
posted 31st May 2024
Did you know that poor data can cost the construction industry in excess of £69 billion each year? Inaccurate data increases the risk of creating delays, having to redo work, and overrunning on budgets. To avoid these risks, surveyors use 3D laser scanners. It is the one tool that can collect accurate data, thanks to the latest technology. It captures digital information regarding the area, enabling contractors to understand the site conditions, eliminating the risk of delays, reworking, and budget overruns.
Measuring Accuracy
Accuracy is comparing the measured value to the real value. There are a number of ways this can be achieved using 3D laser scanning, including:
- Millimetres – Millimetres directly measures any deviation to the real value to ensure accuracy
- Sigma – This is the most common for measurement accuracy. It has proven to be accurate and read as one sigma value.
- Parts in X – This is the accuracy of photogrammetry, dependent on the scale and how it is used.
What Will Impact the Accuracy of 3D Scanners?
Accuracy can be impacted by a number of aspects. When it comes to accuracy, the following points need to be taken into consideration:
- Scanner distance to area to be scanned. The distance is related to the size of the area There is a compromise between accuracy and distance. The further away you scan, the less accurate it will be. The closer the scan, the more accurate it becomes
- Technology used. Even the best technologies can result in inaccuracies if it is not used for the application it is intended.
Technologies Used
There is not one-size-fits-all when it comes to 3D laser scanning. Many of the technologies will provide similar accuracies, though it's important to be aware of the differences. These differences includes Lidar, which is Light Detection and Ranging systems. They are sometimes referred to as laser scanners, but they have different uses. They provide 1cm to 3cm accuracy, with some studies showing a fifteen centimetre accuracy for elevation data in open areas.
Photogrammetry is the next technology used. This technology has the ability to capture textures and shapes, because it uses photography. The accuracy of this technology is determined by the hardware and software used. Contact scanning is a technology that offers excellent accuracy. While it is exceptionally accurate, as it actually touches the object, there are problems that are known to arise, often due to operator error.
Hand Held or on a Tripod
Hand held 3D scanners require skill and experience to achieve accurate results, while tripods and articulated arms are much easier to use, offering consistent results. Even articulating arms can have problems from time to time, they are known to have small deviations, that need to be taken into consideration.
Will Lighting Impact Accuracy?
When it comes to measuring an area, whether indoors or outdoors, lighting is an important consideration, especially when choosing the best 3D laser scanner technology. Photogrammetry relies on lighting to achieve the highest accuracy. If you take the pictures in bright light, the software has a hard time matching and overlapping the pictures, reducing its accuracy. Textured objects also need to be measured in the right lighting when it comes to photogrammetry.
Laser scanning is not only impacted by the light of the area, but also by the light given off by the scanner itself. Light comprises of various wavelengths, which can cause interference with the 3D scans.
In Conclusion
3D laser scanners are an excellent technology when it comes to taking measurements of your property, both inside and outside. With experienced operators that have the knowledge and skill, you can rest assured your scans will be accurate, giving you peace of mind when it comes to your building project.